The bond valence method (or bond valence sum) (not to be mistaken with the valence bond theory in quantum chemistry) is a technique used in coordination chemistry to estimate the oxidation/valence states of atoms.
The basic idea is that the valence Vi of an atom i is the sum of the individual bond valences vij of the Ni surrounding atoms:
| Vi = |
(1) |
The individual bond valences vij are calculated using:
vij = exp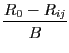 |
(2) |
or
| vij = |
(3) |
Rij is the computed bond length between atoms i and j, R0, B and N are tabulated [a, b, c].
I.S.A.A.C.S. may compute bond valence sums for atomic species/coordination spheres selected by the users.
- a
- http://www.ccp14.ac.uk/ccp/web-mirrors/i_d_brown/bond_valence_param
- b
- I.D. Brown and D. Altermatt
Acta. Cryst., B41:244-247 (1985). - c
- I.D. Brown and R.D. Shannon
Acta. Cryst., A29:266-282 (1973).

|
|