Atomic radii
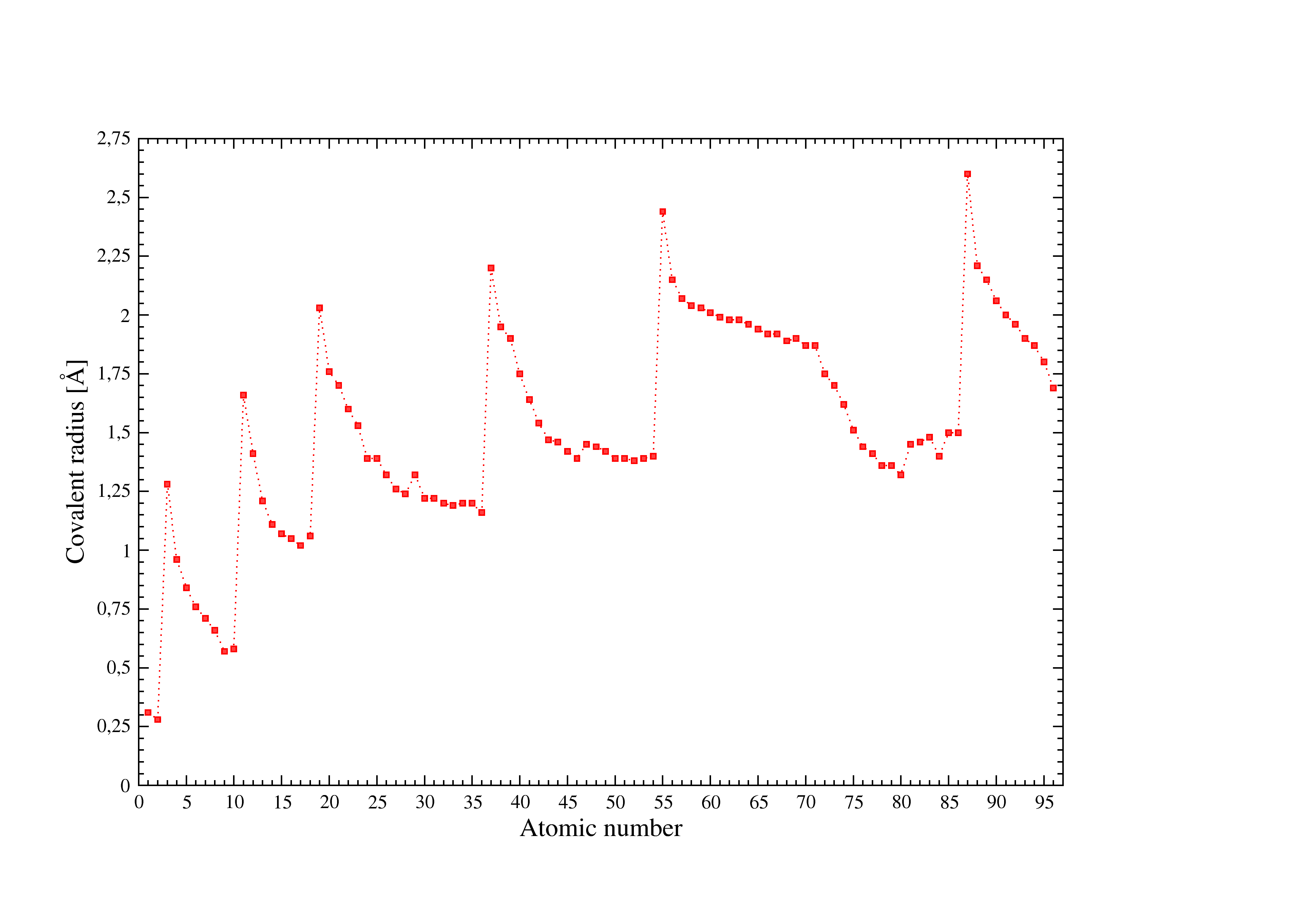
Figure 1:Covalent radii used in I.S.A.A.C.S.
Figure [Fig. 1] illustrates the covalent radii used in I.S.A.A.C.S. see [a] for details.
- a
- Beatriz Cordero and Al. in "Covalent radii revisited"
Dalton Trans.: 2832 - 2838 (2008). [DOI: 10.1039/b801115j]
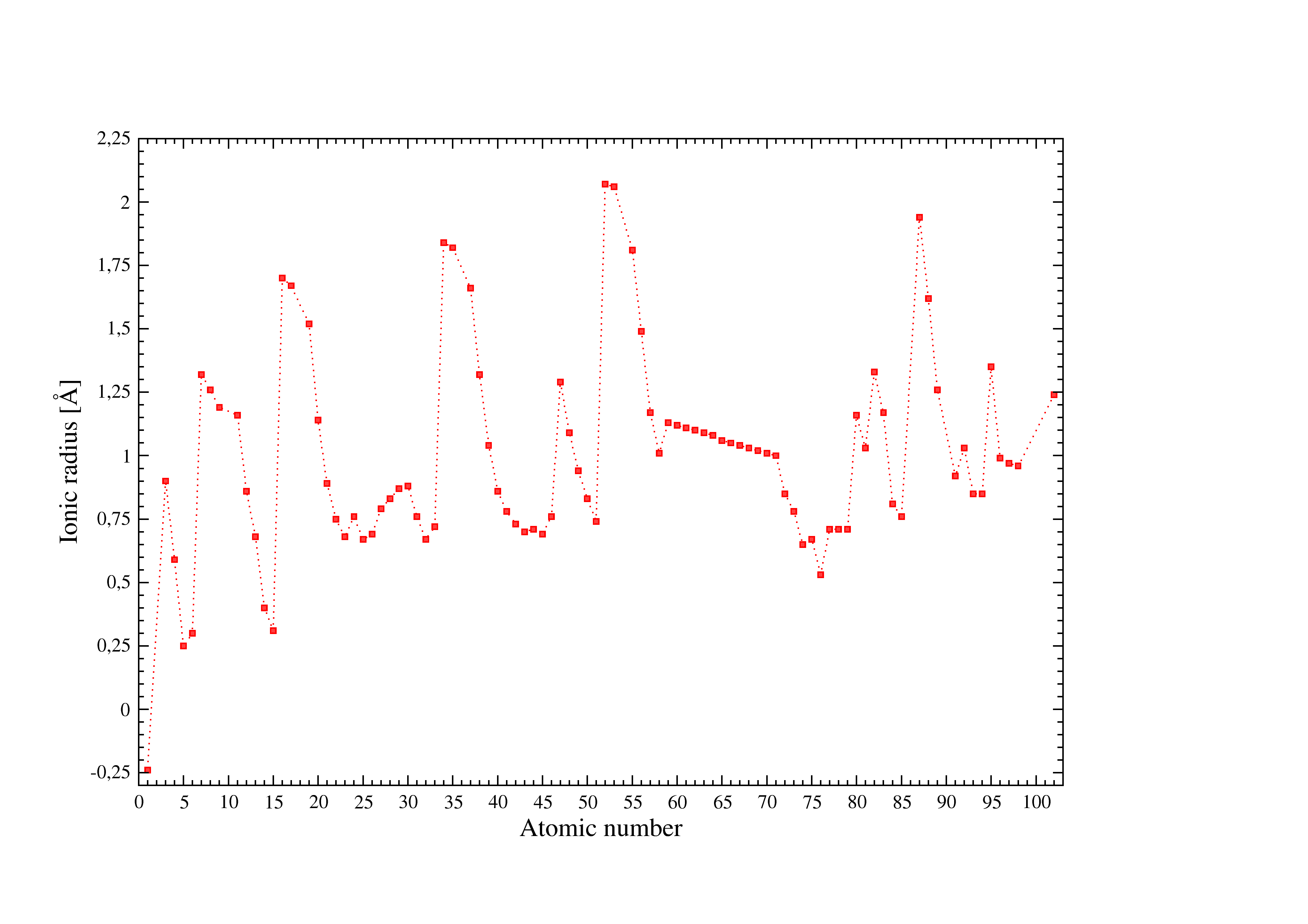
Figure 2:Ionic radii used in I.S.A.A.C.S.
Figure [Fig. 2] illustrates the ionic radii used in I.S.A.A.C.S. see [b] for details.
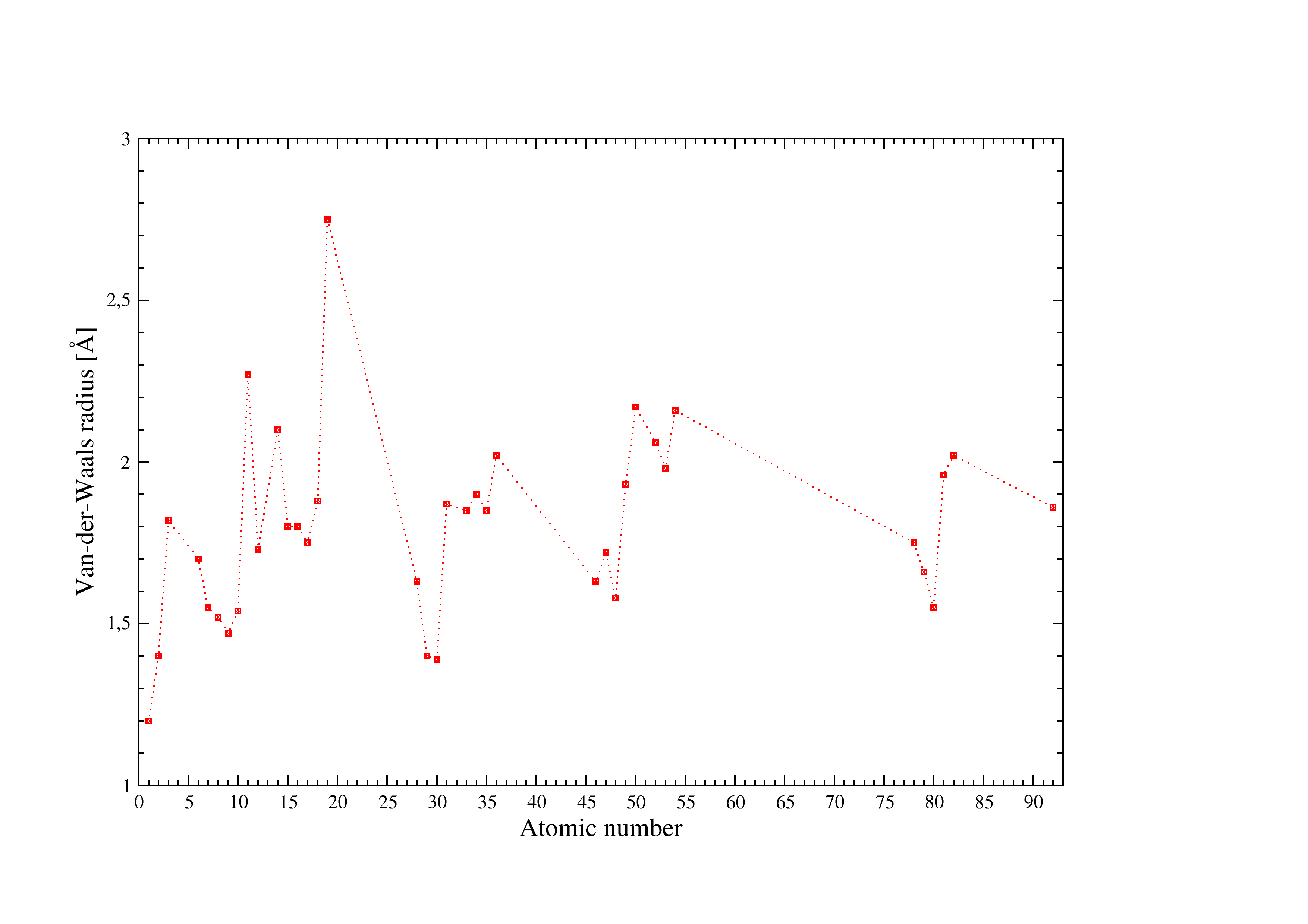
Figure 3:Van Der Waals radii used in I.S.A.A.C.S.
Figure [Fig. 3] illustrates the Van Der Waals radii used in I.S.A.A.C.S. see [c] for details.
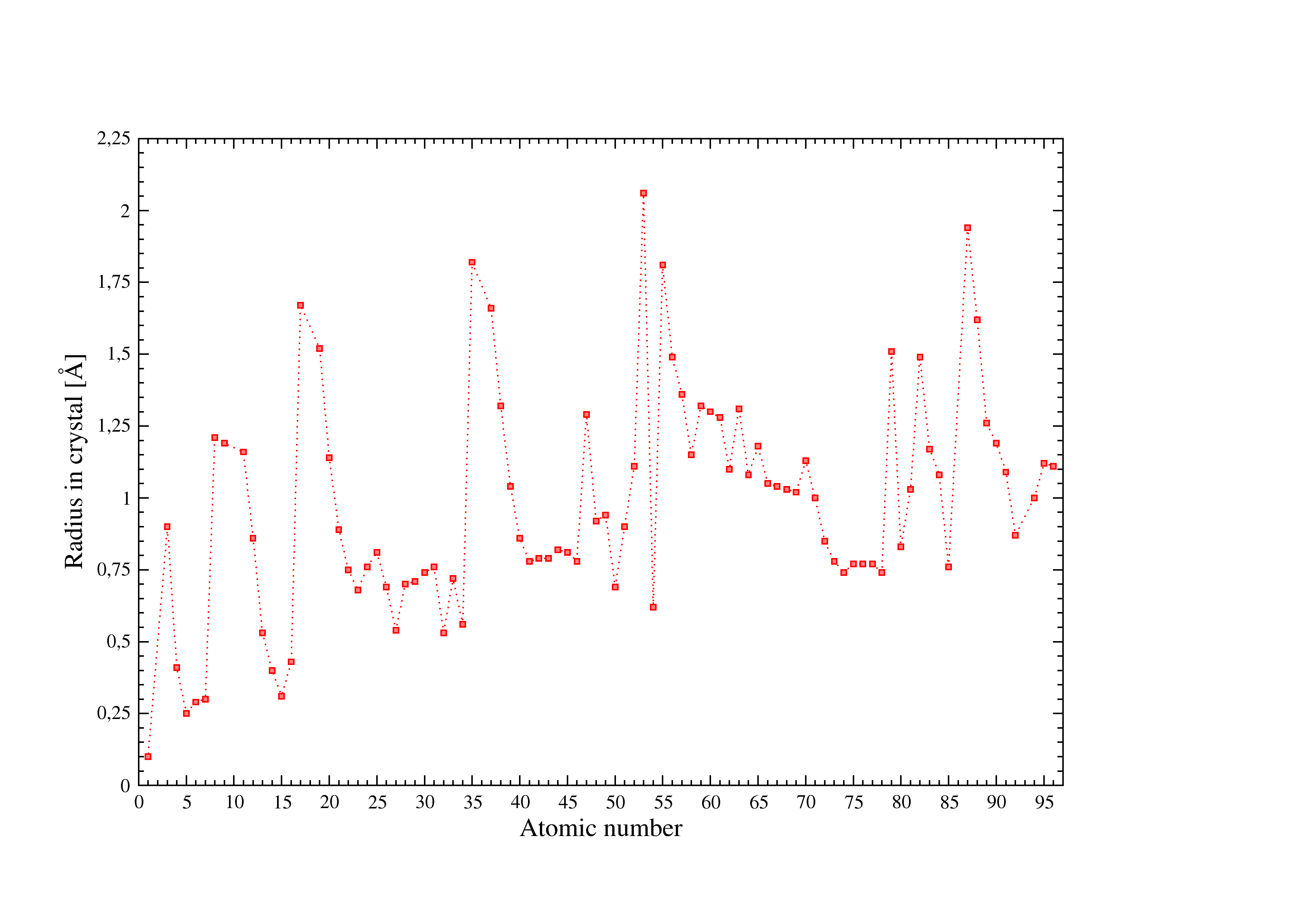
Figure 4:Shannon radii in crystals used in I.S.A.A.C.S.
Figure [Fig. 4] illustrates the atomic radii in crystals compiled by Shannon used in I.S.A.A.C.S. see [d,e] for details.
- d
- Shannon R.D. and Prewitt C.T.
Acta Cryst., B25:925 (1969). - e
- Shannon R.D.
Acta Cryst., A23:751-76A (1976).
Neutron scattering lenghts
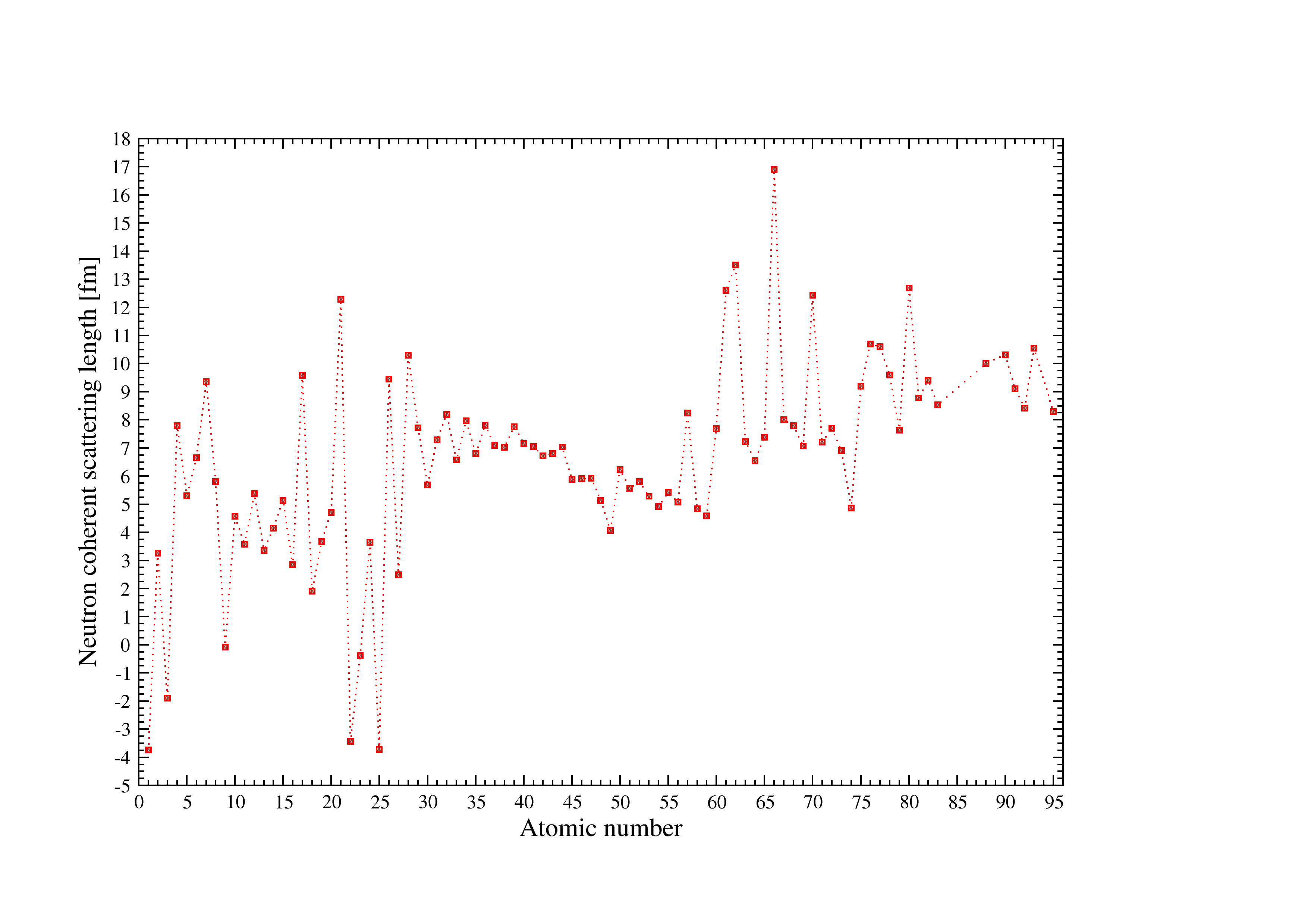
Figure 5:Neutron scattering lengths used in I.S.A.A.C.S.
Figure [Fig. 5] illustrates the neutron scattering lengths used in I.S.A.A.C.S. see [f, g] for details. The atomic numbers are used for the x-ray scattering lengths.
- f
- http://www.ncnr.nist.gov/resources/n-lengths/
- g
- Sears, Varley F.
Neutron News, 3(3):26-37 (1992).
Notes:
Please notice that the user may override the atomic radii as well as the scattering lenghts suggested by I.S.A.A.C.S. and use his/her own.

|
|